What is Liver disease?
Liver disease is a term for a collection of conditions, diseases, and infections that affect the cells, tissues, structures, or functions of the liver.
What is going on in the body?
The liver is an important organ located in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. It is responsible for:
- filtering the blood
- making bile, a substance that helps digest fat and excrete certain fatty substances
- processing and hooking fats to carriers (including cholesterol), and storing sugars, helping the body transport and save energy.
- making important proteins, such as most of those involved in blood clotting
- metabolizing many medications, such as barbiturates, sedatives, and amphetamines
- storing iron, copper, vitamins A and D, and several of the B vitamins
- making important proteins like albumin that regulate fluid transport in the blood and kidneys.
- helping break down and recycle red blood cells
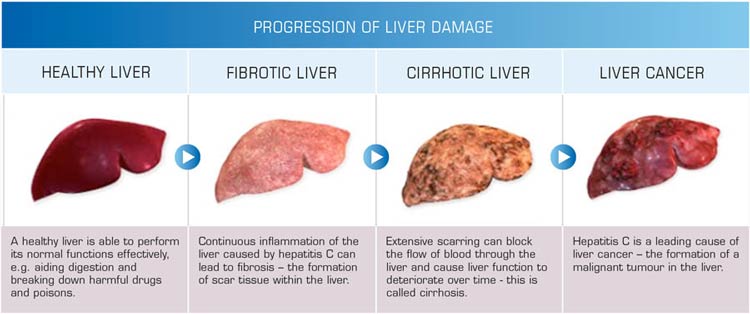
What are the long-term effects of the disease?
Long- term effects depend on the type of liver disease present. For example, chronic hepatitis can lead to:
• cirrhosis of the liver
• liver failure
• illnesses in other parts of the body, such as diabetes, kidney damage or low blood counts
Other long-term effects of liver disease may include:
• gastrointestinal bleeding. This includes bleeding esophageal varices, which are abnormally enlarged veins in the esophagus and/or the stomach.
• encephalopathy, which is deteriorating brain function that may progress to a coma
• peptic ulcers, which erode the stomach lining
• liver cancer
Liver diseases can be treated successfully by concentrated stem cells
Contact Section
To learn more contact us