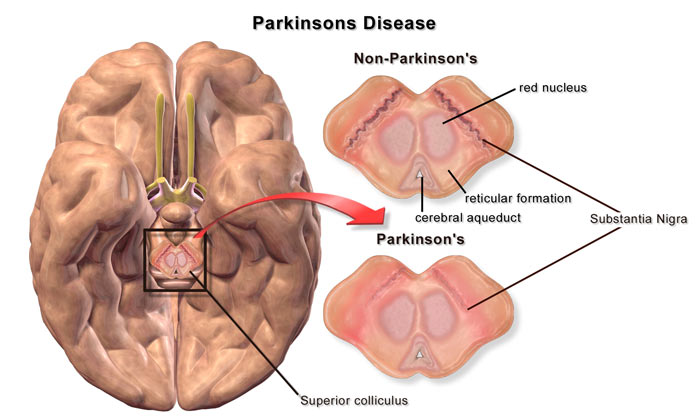
- Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a movement disorder. It is characterized by muscle rigidity, tremor and a slowing of physical movement. This is caused by the degenerative character of the disease, which primarily affects the central nervous system and leads to an impairment of motor and speech skills and a number of other body functions.
Symptoms usually show up in one or more of four ways:
- tremor, or trembling in hands, arms, legs, jaw, and face
- rigidity, or stiffness of limbs and trunk
- bradykinesia, or slowness of movement
- postural instability or impaired balance and coordination
Parkinson’s disease is usually treated with drugs designed to mask its symptoms, thus helping patients live a more normal life, for a while. But eventually, the drugs become ineffective as the disease worsens.
Stem Cell Treatment
The Parkinson’s stem cell treatment differs from standard methods because, in contrast to temporarily masking symptoms with drugs or implanted devices, it is a drug-free alternative focused on affecting humoral and physical changes in the brain, which can improve a patient’s quality of life.
Parkinson’s patients are treated by injecting the stem cells into the bloodstream by lumbar puncture.
Step 1 – Bone Marrow Collection
Each patient’s own bone marrow is collected by withdrawal into syringes that are inserted through the skin on the back and into the hip bones. This procedure is performed by an experienced hematologist with an anesthesiologist in a hospital operating room under light general anesthesia. Bone marrow collection typically takes about 30 minutes.
Bone marrow collection widely known to be safe and many patients do not find it to be painful – during or even after the process.
Step 2 – Laboratory Processing
The stem cells are processed from the bone marrow in a state-of-the-art, government approved (cGMP) laboratory. In the lab, both the quantity and quality of the stem cells are measured. These cells have the potential to transform into multiple types of cells and are capable of regenerating or repairing damaged tissue.
Step 3 – Stem Cell Implantation
The stem cells are implanted back into the patient by lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture as needed
Depending on the treatment needed, The Cord Blood derived or bone marrow concentrate with stem cells are reimplanted to the patient by lumbar puncture. The spinal needle is inserted into the spinal vertebra (between L4 and L5) under local anaesthesia and a small amount of spinal fluid is removed. One part of the spinal fluid is mixed with the bone marrow concentrate with stem cells solution. This mixed solution in turn is injected back into the patients spinal fluid. After the treatment the patient is advised to remain for a few hours in the recovery room.
To learn more please contact us